本文来自:https://www.tomshardware.com/how-to/windows-disable-restart-after-bsod
1.找到 Advanced System Settings
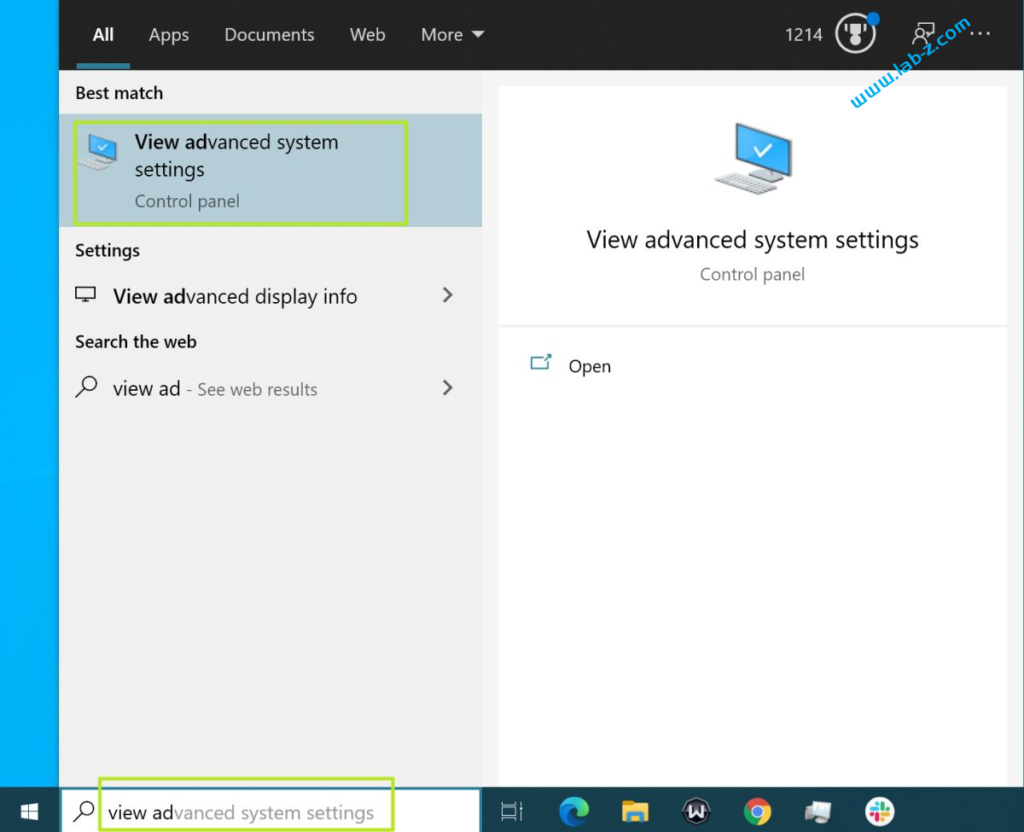
2.切换到“”Start Up and Recovery”页面
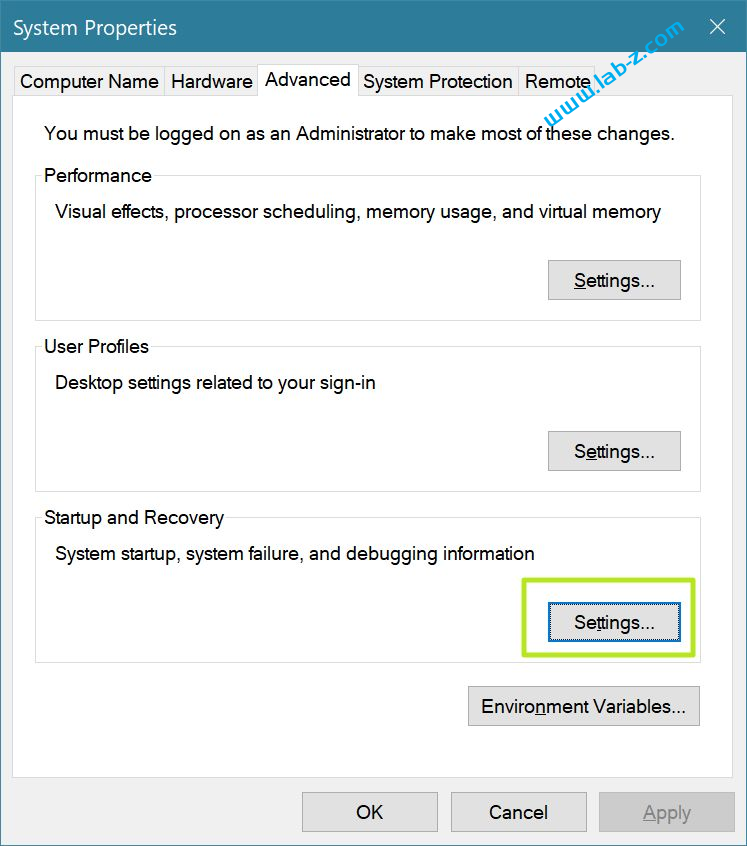
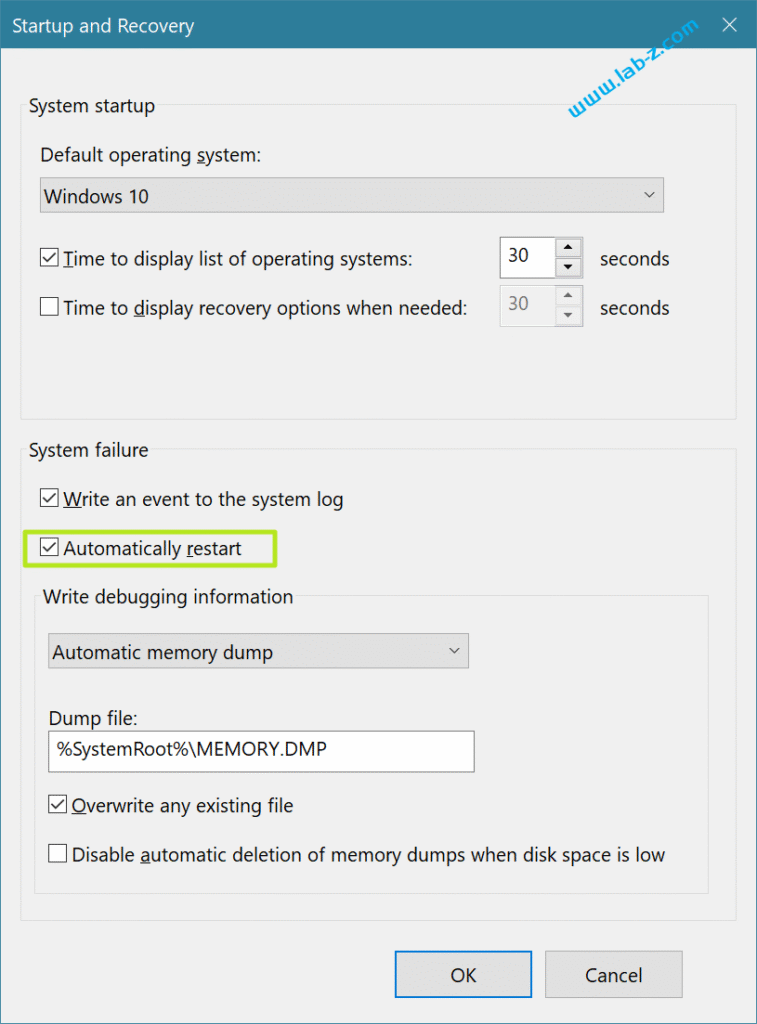
3.找到“Automatically restart” 选项,前面打勾是出现 BSOD 生成完成 Dump 后自动重启,去掉勾之后会停在蓝屏界面
本文来自:https://www.tomshardware.com/how-to/windows-disable-restart-after-bsod
1.找到 Advanced System Settings

2.切换到“”Start Up and Recovery”页面

3.找到“Automatically restart” 选项,前面打勾是出现 BSOD 生成完成 Dump 后自动重启,去掉勾之后会停在蓝屏界面

ESP32 目前支持 I2C 的 Slave Mode ,就是说可以作为一个 I2C 设备存在。
具体的介绍在下面能看到,是一个大佬写了一个 Slave Mode 的库,后来整合到了官方 Release 中。
安装完最新的ESP32 Arduino支持包之后,可以在下面的路径中看到:
C:\Users\UserName\AppData\Local\Arduino15\packages\esp32\hardware\esp32\2.0.6\libraries\Wire
其中的 WireSlave 就是实现一个 I2C Slave 的完整例子。
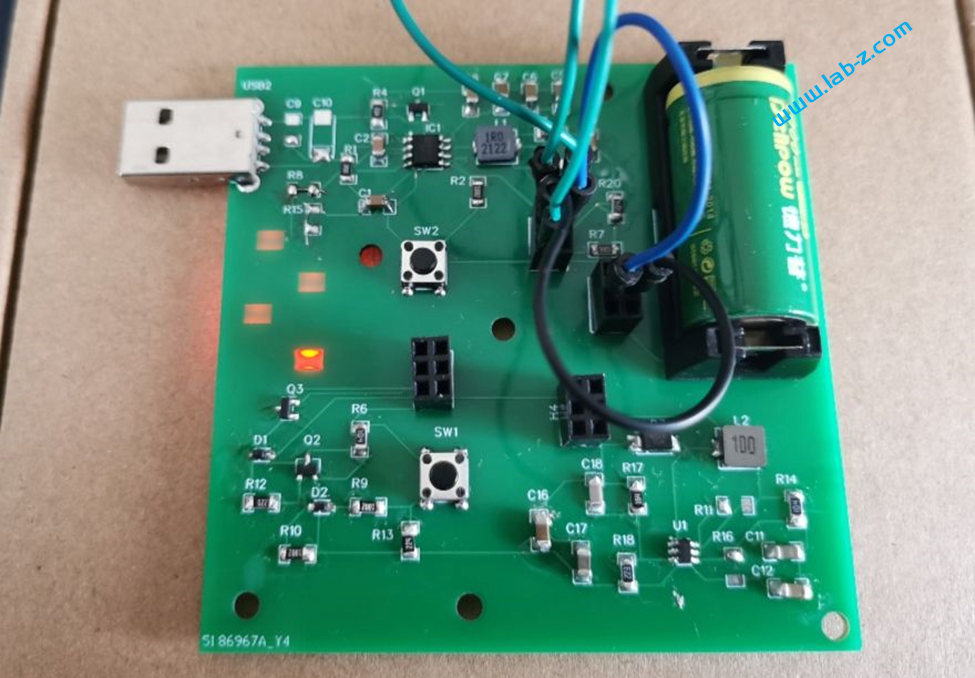
这是一个电路测试板,能够实现下面的功能:
整体电路图如下,可以看到分成四部分:锂电池充放电(第一部分),一键开机和MCU关机(第二部分)、5V升压(第三部分)和锂电池座(第四部分):

首先介绍第一部分,核心是 IP5306模块,接口部分定义如下:

| 引脚 | 功能 | 介绍 |
| 1 | USBIN | Pin1是 USBIN ,连接 MCU ,设置为 INPUT_PULLUP,当USB充电时,会被拉低;当没有充电时会设置为高。从而MCU通过读取这个GPIO 能够得知当前是否有正在进行充电。IP5306 没有反映当前充电状态的引脚,所使用这个设计来获得充电状态; |
| 2 | OUT1 | Pin2 是5V输出。当没有对外供电时,这里有4V 左右的电压输出;当外部插入取电时,或者SW2按钮按下时,这里会有5V输出; |
| 3 | GND | |
| 4 | BATIN | 连接电池正极输入; |
| 5 | GND | |
| 6 | BAT_ADC | 一个分压输出,MCU 的 ADC 能够获得当前的电池电压信息 |
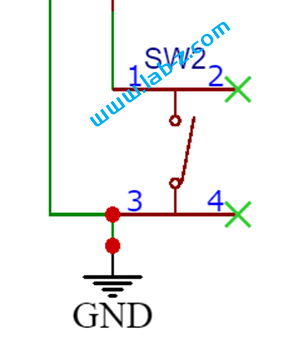
此外这部分的 SW2是一个按钮,短按可以让 IP5306输出5V,再次按下会切断输出,如果负载<50ma,那么 45s之后也会停止输出
接下来是第二部分:
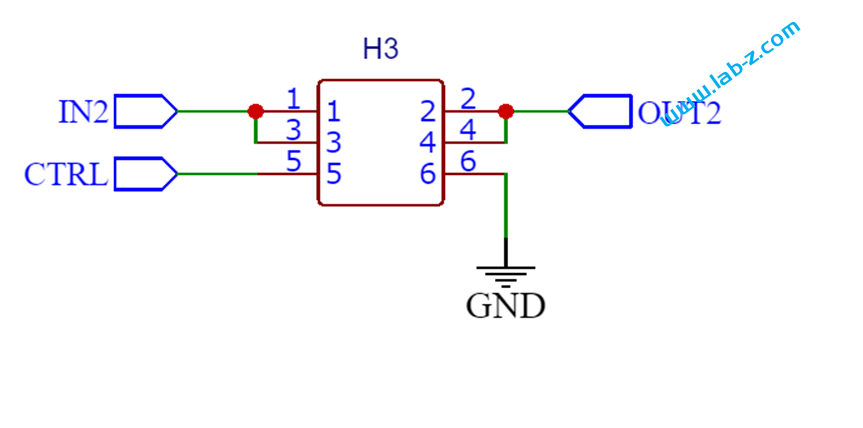
这部分根据【参考1】而来,很好用。接口定义如下:
| 引脚 | 功能 | 介绍 |
| 1 | IN2 | 输入(第一部分输出的OUT1 可以接入这里) |
| 2 | OUT2 | 控制后的输出 |
| 3 | IN2 | 同上 IN2 |
| 4 | OUT2 | 同上 OUT2 |
| 5 | CTRL | 输出控制脚,初始时MCU 需要通过 CTRL对这里输入一个高电平,当需要断电时CTRL输入低电平随即切断Pin2的输出 |
| 6 | GND | |
这部分也带有一个按键,按下之后 Pin2 即可输出(需要按的稍微长一些,保证MCU 的 CTRL能够输出高电平)
第三部分,基于MT3608 芯片的5V升压设计,具体芯片 DataSheet可以在【参考2】看到,这个也是也是来自开源广场别人的设计(不过忘记是哪篇了,找了一下没找到),接口定义如下:
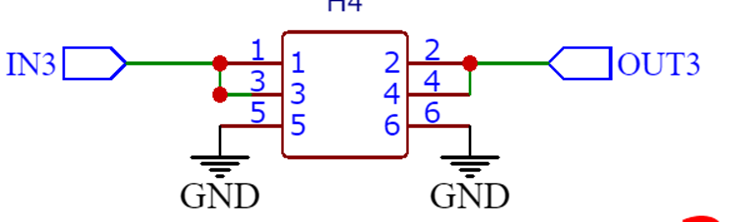
| 引脚 | 功能 | 介绍 |
| 1 | IN3 | 电源输入,例如输入3.3V |
| 2 | OUT3 | 电源输出,5V |
| 3 | IN3 | 同上IN3 |
| 4 | OUT3 | 同上OUT3 |
| 5 | GND | |
| 6 | GND |
简单功耗测量,测试方法是在电池串联万用表测量电流。5V对ESP32 S3 板【参考3】输出时,电流在90ma左右;MCU 切断供电后,电流在5ma左右;经过45s后IP5306自动断电后电流在0.04ma左右。
工作视频在:
上述主要芯片除了电容电阻,其余都是购买自立创商城,有兴趣的朋友可以实验。
参考:
前面介绍过在 UEFI 下创建内存虚拟盘的操作,这次介绍如何创建包含需要内容的内存虚拟盘。生成的虚拟盘可以在没有硬盘的情况下充当临时文件的存放位置。当然如果关机或者断电后,盘中内容会消失。
第一步,根据【参考1】制作一个磁盘镜像VHD,这里出于体积考虑,制作了一个 64MB 的FAT32 空盘;
第二步,上面制作磁盘镜像大部分内容都是 0x00(可以看作是以512Bytes为单位的稀疏矩阵),因此我们还需要一个工具提取文件中的非零内容保存起来,这样能够有效降低镜像尺寸。使用 C# 编写代码如下。简单的说就是以512Bytes为单位读取文件,然后检查512 bytes 中是否为全0.如果不是就记录下来保存到文件中。每一个项目是由 4 Bytes 记录加一个 512Byte的数组构成。特别注意 VHD 镜像文件末尾包含了一个文件头,我们这里会对文件大小取整,对于末尾的文件头不会进行处理。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.IO;
namespace ConsoleApp7
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (args.Count() == 0) {
Console.WriteLine("Please input file name!");
Console.ReadKey();
Environment.Exit(0);
}
if (File.Exists((args[0] + ".raw"))) {
File.Delete(args[0] + ".raw");
}
FileStream fs = new FileStream(args[0], FileMode.Open);
FileStream RawFs = new FileStream(args[0]+".raw", FileMode.CreateNew);
byte[] array = new byte[512];
UInt32 Data;
Boolean EmptyMark;
// 写入 Disk Image 的Size (以 1MB 为单位)
Data = (UInt32) fs.Length / 1024 / 1024;
RawFs.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(Data), 0, 4);
// 处理整数以内的磁盘,例如:扫描 64MB 以内的内容生成及镜像
while (fs.Position < fs.Length / 1024 / 1024 * 1024 * 1024) {
EmptyMark = true;
fs.Read(array, 0, array.Length);
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
if (array[i] != 0x00)
{
EmptyMark = false;
break;
}
}
if (EmptyMark==false)
{
Data = (UInt32)(fs.Position / 512 - 1);
RawFs.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(Data),0,4);
RawFs.Write(array, 0, array.Length);
Console.WriteLine("{0}", Data);
}
}
RawFs.Close();
Console.WriteLine("Done!");
}
}
}
例如:64MB的FAT32 空盘,经过上述操作后会变成6K 大小。
第三步,编写Shell 下的 UEFI Application,创建内存虚拟盘,然后读取前述生成的文件,将内容放在虚拟盘中。这样就得到了一个带有文件系统的内存虚拟盘。代码如下:
#include <Library/BaseLib.h>
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/PrintLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <Protocol/RamDisk.h>
#include <Protocol/DevicePathToText.h>
#include <Protocol/HiiDatabase.h>
#include <Protocol/HiiPackageList.h>
#include <Protocol/HiiImageEx.h>
#include <Protocol/PlatformLogo.h>
#include <Protocol/GraphicsOutput.h>
#include <Library/UefiApplicationEntryPoint.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiBootServicesTableLib.h>
#include <Library/BaseMemoryLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
//DO NOT REMOVE IMAGE_TOKEN (IMG_LOGO)
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
UefiMain (
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *SystemTable
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_RAM_DISK_PROTOCOL *MyRamDisk;
EFI_FILE_HANDLE FileHandle;
UINTN tmp, DiskSize,SectorIndex;
UINT64 *StartingAddr,Position;
UINT8 Sector[512];
UINTN ImageFileSize;
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *DevicePath;
// 磁盘镜像文件
CHAR16 *DiskImage=L"DiskImage.BIN";
// 如果磁盘镜像不存在,报错退出
if (ShellFileExists(DiskImage)!=EFI_SUCCESS)
{
Print(L"Couldn't find 'DiskImage.bin'\n");
return EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER;
}
// 打开磁盘镜像文件
Status = ShellOpenFileByName(
DiskImage,
(SHELL_FILE_HANDLE *)&FileHandle,
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ,
0);
if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS)
{
Print(L"OpenFile failed!\n");
return EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER;
}
// Look for Ram Disk Protocol
Status = gBS->LocateProtocol (
&gEfiRamDiskProtocolGuid,
NULL,
&MyRamDisk
);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status))
{
Print(L"Couldn't find RamDiskProtocol\n");
return EFI_ALREADY_STARTED;
}
tmp=4;
Status = ShellReadFile(FileHandle,&tmp,&DiskSize);
Print(L"Disk size %dMB\n",DiskSize);
DiskSize=DiskSize*1024*1024;
//Allocate a memory for Image
StartingAddr = AllocateReservedZeroPool ((UINTN)DiskSize);
if(StartingAddr==0)
{
Print(L"Allocate Memory failed!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
ShellGetFileSize(FileHandle,&ImageFileSize);
Position=0;
Print(L"File size %d\n",ImageFileSize);
while (Position<ImageFileSize)
{
tmp=4;
Status = ShellReadFile(FileHandle,&tmp,&SectorIndex);
if (Status!=EFI_SUCCESS)
{
break;
}
Print(L"Sector index %d\n",SectorIndex);
tmp=512;
Status = ShellReadFile(FileHandle,&tmp,&Sector);
if (Status==EFI_SUCCESS)
{
//Print(L"Read success %d\n",(UINT8*)StartingAddr+SectorIndex*512);
CopyMem((UINT8*)StartingAddr+SectorIndex*512,&Sector,tmp);
}
ShellGetFilePosition(FileHandle,&Position);
//Print(L"postion %d\n",Position);
}
//
// Register the newly created RAM disk.
//
Status = MyRamDisk->Register (
((UINT64)(UINTN) StartingAddr),
DiskSize,
&gEfiVirtualDiskGuid,
NULL,
&DevicePath
);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status))
{
Print(L"Can't create RAM Disk!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
ShellCloseFile(&FileHandle);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
基本思路就是:打开镜像文件读取4 Bytes,然后创建这个大小的 Memory Disk。接下来读取 4 Bytes的扇区位置,然后再读取512字节的扇区内容,将这个内容存放在内存中的对应位置。
在Shell 下执行这个程序后,使用 map -r 即可看到新生成的内存盘。
UEFI 代码和编译后的EFI 文件,同时内置了一个64MB的磁盘镜像。
前面提到的 Windows 下的磁盘镜像扫描工具。内置了一个 64MB的空磁盘镜像。
参考:
1. https://www.lab-z.com/vt/
前面提到了如何将 MemTest86 打包为一个 EFI 文件,美中不足的是运行这个 EFI 之后无法自动跳转到 Memtest86中执行,还需要手工运行map 和执行。针对这个问题增加代码进行实验。
新增的代码如下:
1.代码从创建 RAM Disk 开始
//
// Register the newly created RAM disk.
//
Status = MyRamDisk->Register (
((UINT64)(UINTN) StartingAddr),
FileSize,
&gEfiVirtualDiskGuid,
NULL,
&DevicePath
);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status))
{
Print(L"Can't create RAM Disk!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
2.使用 ShellExecute 来运行 map -r 命令
Print(L"Running map -r command!\n");
CHAR16 *MapCommmand=L"map -r";
EFI_STATUS CmdStat;
Status = ShellExecute( &gImageHandle, MapCommmand, FALSE, NULL, &CmdStat);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status))
{
Print(L"Can't run MAP command\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
Print(L"%r\n",CmdStat);
3.接下来扫描所有的 FSx: 。如果存在某个FSx::\efi\boot\mt86.png,那就说明是 MemTest86 的盘。
UINTN i;
CHAR16 StrBuffer[80];
BOOLEAN Found=FALSE;
for (i=0; i<9; i++)
{
UnicodeSPrint(StrBuffer,sizeof(StrBuffer),L"fs%d:\\efi\\boot\\mt86.png",i);
Print(L"%s\n",StrBuffer);
if (!EFI_ERROR(ShellFileExists(StrBuffer)))
{
UnicodeSPrint(StrBuffer,sizeof(StrBuffer),L"fs%d:\\efi\\boot\\BootX64.EFI",i);
Found=TRUE;
break;
}
}
if (Found)
{
ShellExecute( &gImageHandle, StrBuffer, FALSE, NULL, NULL);
}
return 0;
上述设计逻辑没有问题,但是测试发现无法达到预期的目标:MemTest86 不会自动运行起来。执行之后,仍然需要手工运行 Map -r ,然后找到新生成的 FsX:再进入执行。
于是进行调试,从ShellExecute()函数入手。
这个函数定义在 \ShellPkg\Library\UefiShellLib\UefiShellLib.c 这个文件中。
/**
Cause the shell to parse and execute a command line.
This function creates a nested instance of the shell and executes the specified
command (CommandLine) with the specified environment (Environment). Upon return,
the status code returned by the specified command is placed in StatusCode.
If Environment is NULL, then the current environment is used and all changes made
by the commands executed will be reflected in the current environment. If the
Environment is non-NULL, then the changes made will be discarded.
The CommandLine is executed from the current working directory on the current
device.
The EnvironmentVariables pararemeter is ignored in a pre-UEFI Shell 2.0
environment. The values pointed to by the parameters will be unchanged by the
ShellExecute() function. The Output parameter has no effect in a
UEFI Shell 2.0 environment.
@param[in] ParentHandle The parent image starting the operation.
@param[in] CommandLine The pointer to a NULL terminated command line.
@param[in] Output True to display debug output. False to hide it.
@param[in] EnvironmentVariables Optional pointer to array of environment variables
in the form "x=y". If NULL, the current set is used.
@param[out] Status The status of the run command line.
@retval EFI_SUCCESS The operation completed sucessfully. Status
contains the status code returned.
@retval EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER A parameter contains an invalid value.
@retval EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES Out of resources.
@retval EFI_UNSUPPORTED The operation is not allowed.
**/
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
ShellExecute (
IN EFI_HANDLE *ParentHandle,
IN CHAR16 *CommandLine OPTIONAL,
IN BOOLEAN Output OPTIONAL,
IN CHAR16 **EnvironmentVariables OPTIONAL,
OUT EFI_STATUS *Status OPTIONAL
)
从Log可以看到执行的是下面这段代码:
//
// Check for UEFI Shell 2.0 protocols
//
if (gEfiShellProtocol != NULL) {
//
// Call UEFI Shell 2.0 version (not using Output parameter)
//
return (gEfiShellProtocol->Execute (
ParentHandle,
CommandLine,
EnvironmentVariables,
Status
));
}
进一步追踪,执行的是 \ShellPkg\Application\Shell\ShellProtocol.c定义的如下:
// Pure FILE_HANDLE operations are passed to FileHandleLib
// these functions are indicated by the *
EFI_SHELL_PROTOCOL mShellProtocol = {
EfiShellExecute,
EfiShellGetEnv,
……
};
具体实现在 \ShellPkg\Application\Shell\ShellProtocol.c文件中:
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
EfiShellExecute (
IN EFI_HANDLE *ParentImageHandle,
IN CHAR16 *CommandLine OPTIONAL,
IN CHAR16 **Environment OPTIONAL,
OUT EFI_STATUS *StatusCode OPTIONAL
)
运行方式如下:
Temp = NULL;
Size = 0;
ASSERT ((Temp == NULL && Size == 0) || (Temp != NULL));
StrnCatGrow (&Temp, &Size, L"Shell.efi -exit ", 0);
StrnCatGrow (&Temp, &Size, CommandLine, 0);
Status = InternalShellExecuteDevicePath (
ParentImageHandle,
DevPath,
Temp,
(CONST CHAR16 **)Environment,
StatusCode
);
Status = InternalShellExecute (
(CONST CHAR16 *)CommandLine,
(CONST CHAR16 **)Environment,
StatusCode
);
从代码上看,出现问题的原因是:默认情况下(允许 嵌套/NEST),ShellExecute()运行的 MAP 命令会通过 “shell.efi map -r ”的方式运行,这样相当于重新启动了一个 Shell ,在新启动的 Shell 中执行了 map -r,运行完成后会返回调用者处于的 shell 中,之前的 map 加载出现的 Fsx:盘符失效,所以无法看到新添加的 fsx:。
解决方法:通过 shell.efi -nonest 参数启动 Shell ,这个 Shell 禁止了 Nest ,再次运行 mrd3 调用的 map -r 就是对于当前shell。
完整代码下载:
编译后的 EFI Application 下载:
串口是最常见的接口,因为它足够简单,几乎在所有的调试场合都能看到它的身影。从编程的角度来说,这种接口的代码已经非常成熟,从 C 到 Python 都能够支持这种接口。实际工作生产中最常见的就是USB转串口。美中不足的是,这USB转串口在编程的时候存在着如下缺陷:
针对上述问题,这次使用南京沁恒微电子公司出品的 CH32V208 制作一个双USB串口数据交换器(Dual USB SERIAL DATA EXCHANGER, 简称DUSDE)。CH32V208是一款基于32位RISC-V设计的无线型微控制器,配备了硬件堆栈区、快速中断入口,在标准RISC-V基础上大大提高了中断响应速度。搭载V4C内核,加入内存保护单元,同时降低硬件除法周期。除了片上集成2Mbps低功耗蓝牙BLE 通讯模块、10M以太网MAC+PHY模块、CAN控制器等接口之外还带有2个USB2.0全速设备+主机/设备接口。这次的双USB串口数据交换器就是将自身模拟为2个 USB 串口设备分别连接到两台电脑上,从而实现数据传输的功能。

从上面的系统结构图可以看到,CH32V208WBU6支持两个USB2.0 Full Speed设备,其中一个可以作为 HOST或者Device,另外一个只能作为 Device 使用。我们通过编程的方式,让他们都工作在Device 模式下,下图就是我们设备的框图。

针对前面的需要额外驱动的问题,通过编程在DUSDC上实现USB CDC协议,这样在Windows 8 及其以上的系统无需额外安装驱动。Windows 识别所属的 Class 之后,会自动加载内置驱动。
针对多个串口和需要检测对面设备是否准备好的问题,我们预定义了一些命令,当用户使用2022波特率打开串口后,能够响应如下命令。
| 方向 | 命令 | 返回值 | 用途 |
| PC->Device | ?ACV | USB1 或者 USB2 | 设备测试。返回当前的USB接口名称 |
| PC->Device | ?VER | 例如:0003 | 查询当前固件版本。返回当前固件版本信息,例如:0003 这种版本号 |
| PC->Device | ?SER | 例如:1234 | 查询设备序列号。返回当前设备的序列号,对于同一个设备,从USB1和USB2读取的序列号相同,例如:1234 |
| PC->Device | ?CFG | NRDY或者REDY | 查询另外一个USB端口是否已经Active。当一个USB Port 收到“?ACV” 命令后就处于 Active 状态了。之后另外一个USB Port 使用这个命令会反馈前一个USB Port的状态 |
例如,系统中存在 COM1 到 COM4 多个串口,程序枚举每一个串口,打开串口后设定波特率为2022,之后从该串口发送“?ACV”命令,如果能够得到“USB1”或者“USB2”这样的回复,会表明当前为1号或者2号USB端口;
再比如,我们用设备连接两台电脑,USB Port1有程序打开过端口,并且用 “?ACV”查询过当前设备,那么USB Port 2这端程序以2022波特率打开端口后,再发送“?CFG”就能得到“REDY”的回复,表示对面的端口(USB1)已经准备好,反之如果收到“NRDY”则表示另外端口没有收到过“?ACV”命令;
最后,在程序看来数据使用串口传输,但是因为所有的传输都是在USB中进行,USB端口之间的数据也是在内存中进行的交换,相比传统串口速度会有很大的提升。实际测试表明在在使用超级终端程序的zmodem 协议传输文件时,速度可达300KB/S以上。同时因为没有串口的发送和采样过程,传输过程发生错误的概率极低。
上面就是为什么要设计DUSDC,以及它的优点。下面介绍DUSDC的具体实现。
首先是硬件部分。整体设计非常简单,并没有太多的元件:
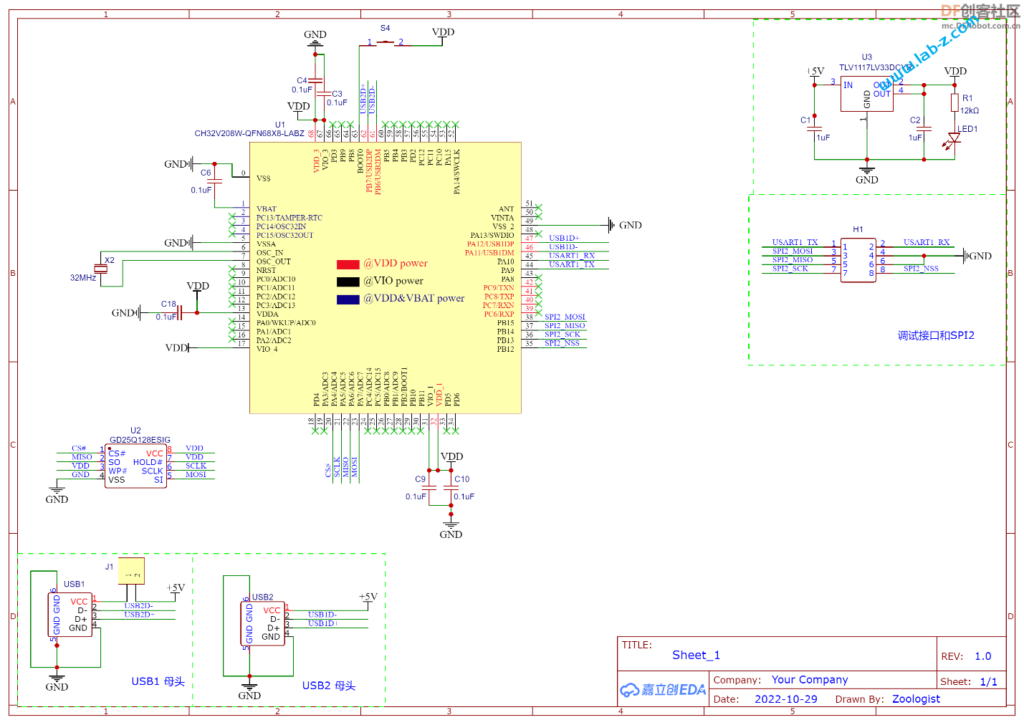
核心部分就是基于CH32V208的最小系统,其中的S4 是Download 按钮,需要下载Firmware时,先按住按钮然后插入USB接口,之后再抬起按钮,使用 WCHISPTool即可下载。
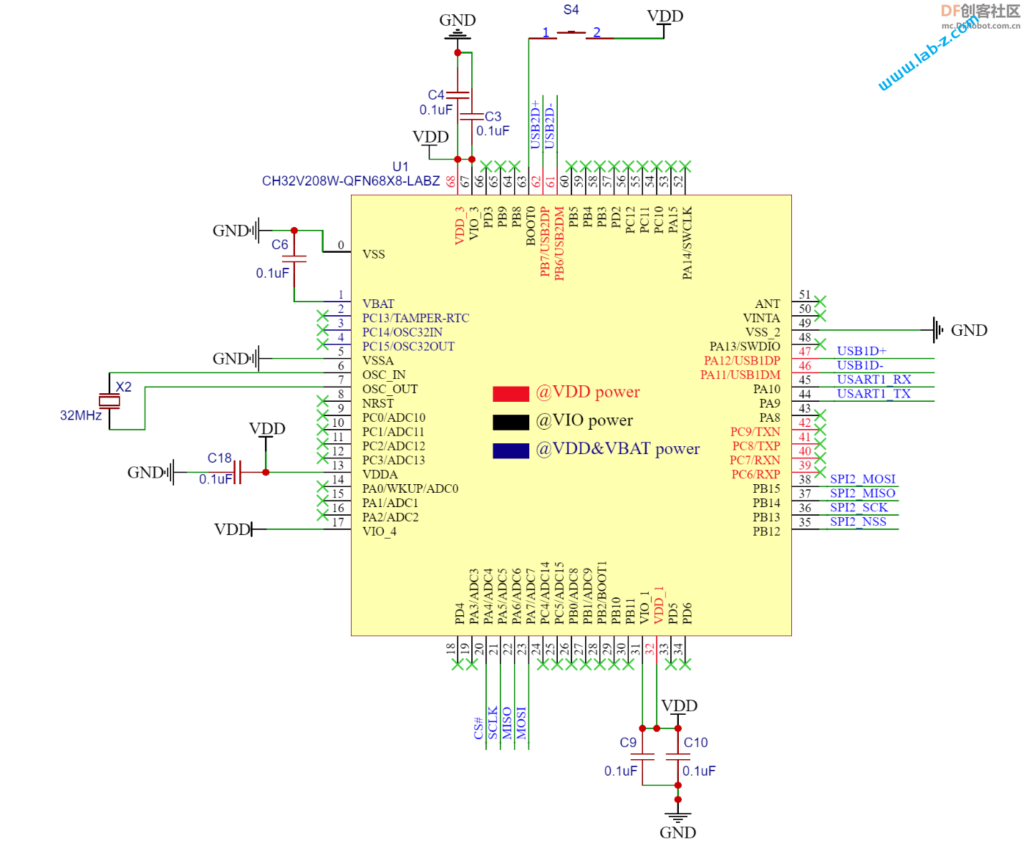
USB 使用的是Type-B 母头,选择原因是这种结构非常稳固,最大限度保证连接的可靠。需要注意的是J1是预留的取电接口,在连接两台PC时,为了避免5V电压不同可以将J1断开,这样设备就只能通过USB2进行取电。
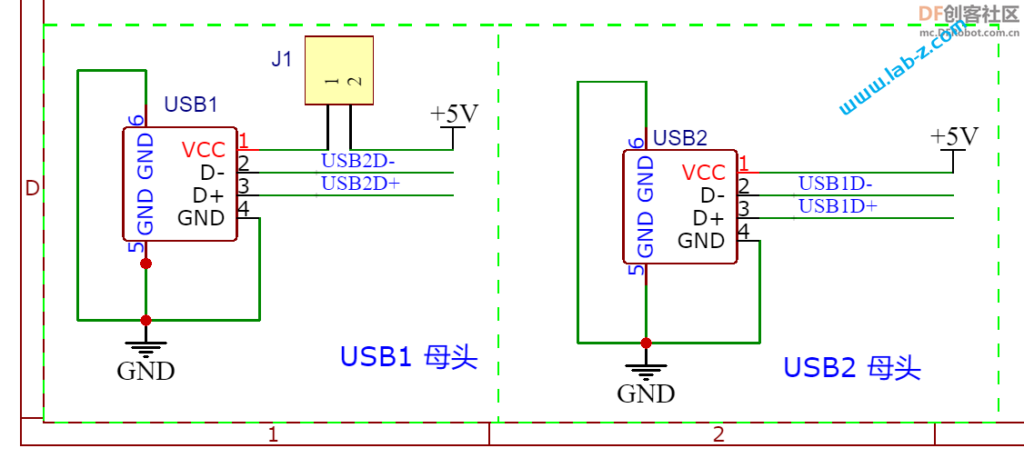
通过一颗TLV1117 来实现5V到3.3V的转换,5V来自USB 端口。预留了UART1作为调试接口,基本上所有的问题都能通过输出 Log 来解决。
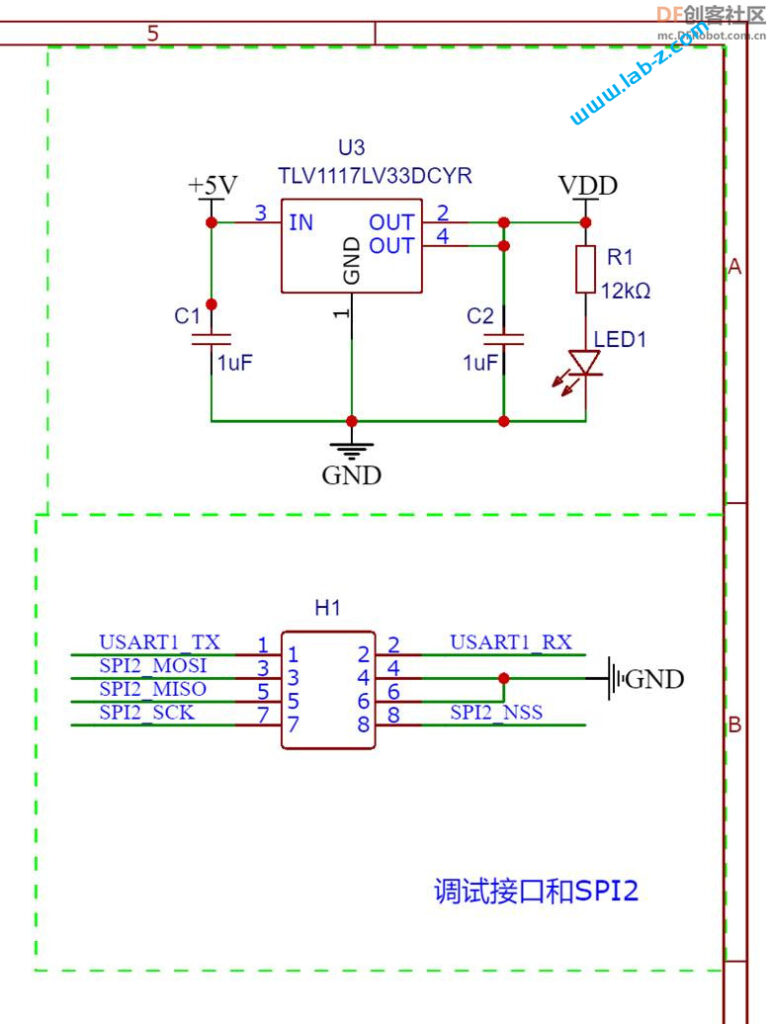
此外,板子上预留了一个SPI1 出来的SPI NOR 接口,如果有记录数据的需求,可以考虑在该位置焊接SPI NOR芯片或者PSRAM。
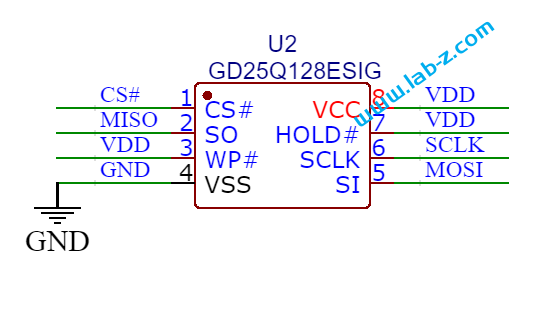
因为板子上没有多余的元件,所以布线也比较简单:
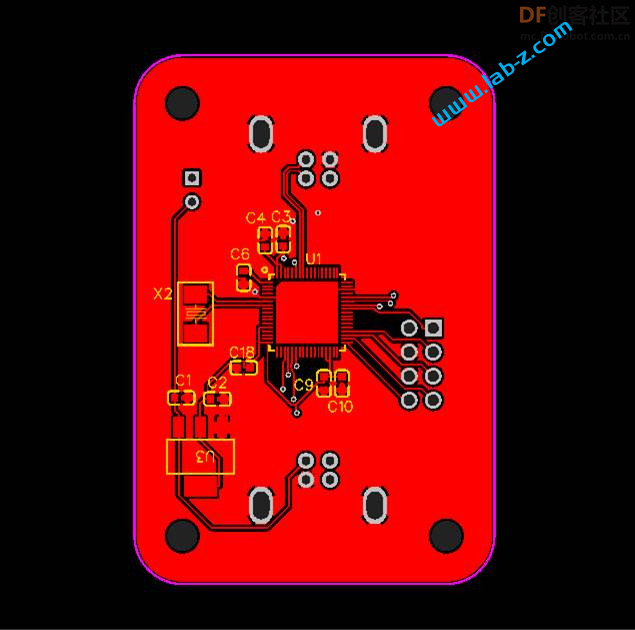
3D渲染结果:
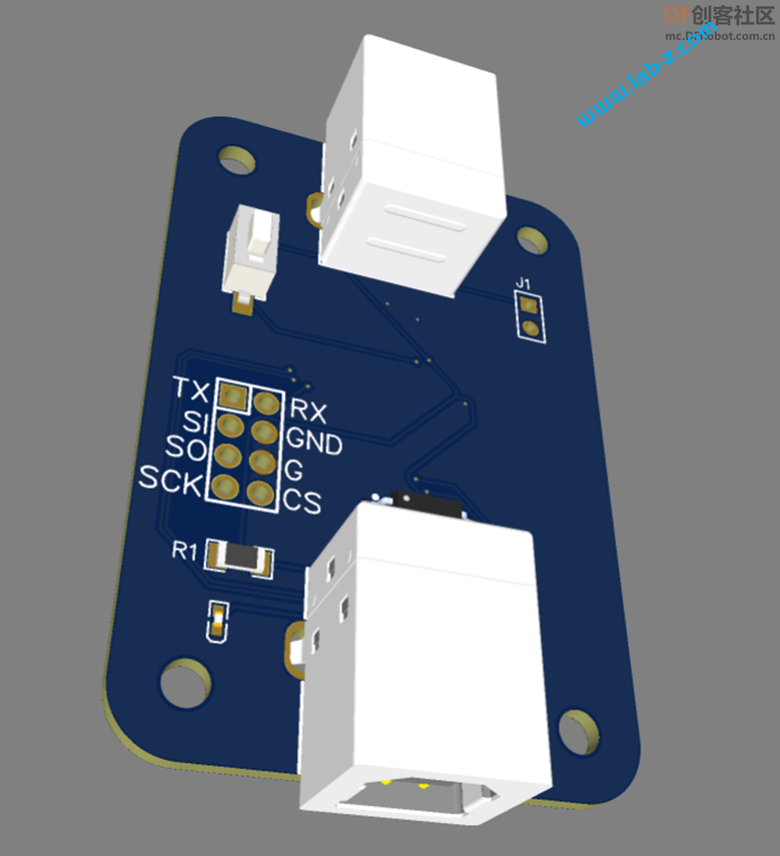
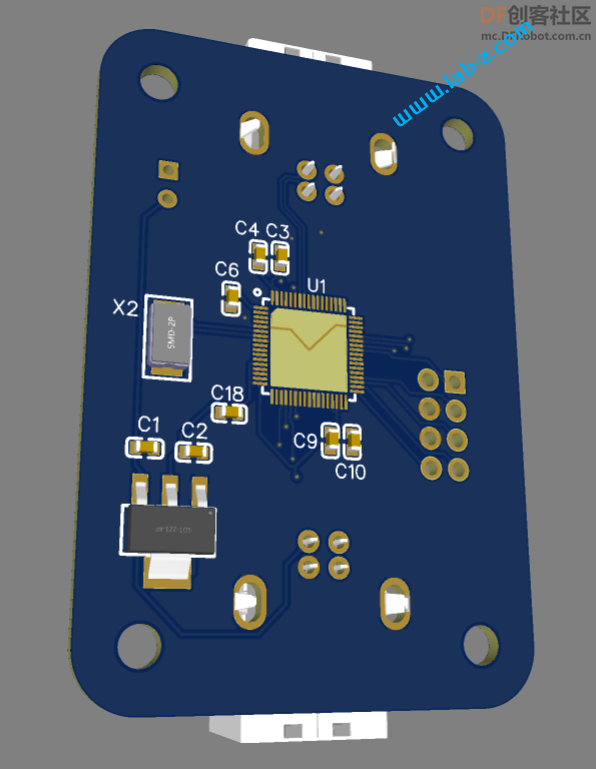
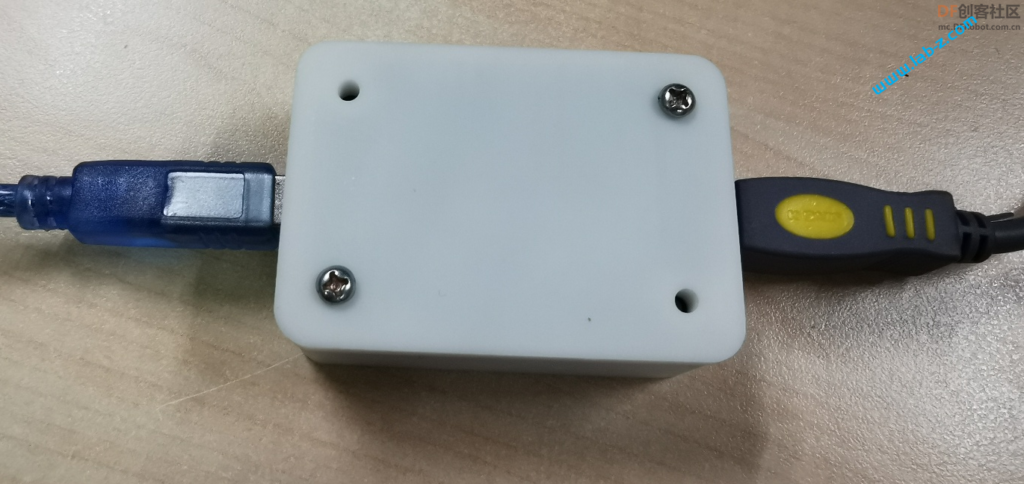
成品PCB:
硬件确定之后就可以着手设计软件了。CH32V208的示例程序有两个USB 转UART的例子,一个是USBDB (全速设备控制器)的例子,另外一个是USBFS(全速主机/设备控制器,这里用作全速设备控制器)。因为功能上有差别,这两个控制器名称也有差别,编程比较麻烦。类似CH567的话,一个是USB1另外一个是USB2感觉就会好很多。第一个工作是将两个代码融合在一起通过编译。
例如,当前是USBDB,工作基本流程是:
注意:USB 中描述的 OUT 和IN 是以HOST的CPU 为准的,对于运行着 Windows的x86 来说,OUT 是指从CPU到单片机方向(Write),反之数据是从单片机到CPU(Read)。
上述过程中, 代码位置简述:
/*********************************************************************
* @fn EP2_OUT_Callback
*
* @brief Endpoint 2 OUT.
*
* @return none
*/
void EP2_OUT_Callback(void) {
//ZivDebug_Start
uint32_t Status;
Status = _GetEPRxStatus(EP2_OUT);
uint16_t USB1BufLen = GetEPRxCount( EP2_OUT & 0x7F);
PMAToUserBufferCopy(&USB1_Tx_Buf[USB1_Tx_Counter], GetEPRxAddr( EP2_OUT & 0x7F),
USB1BufLen);
if (USB1Replay!=0xFF) {
if ((USB1_Tx_Buf[0] == '?') && (USB1_Tx_Buf[1] == 'A')
&& (USB1_Tx_Buf[2] == 'C') && (USB1_Tx_Buf[3] == 'V')) {
printf("RCV ACV CMD\r\n");
USB1Replay = 0x01;
}
if ((USB1_Tx_Buf[0] == '?') && (USB1_Tx_Buf[1] == 'V')
&& (USB1_Tx_Buf[2] == 'E') && (USB1_Tx_Buf[3] == 'R')) {
printf("RCV VER CMD\r\n");
USB1Replay = 0x02;
}
if ((USB1_Tx_Buf[0] == '?') && (USB1_Tx_Buf[1] == 'S')
&& (USB1_Tx_Buf[2] == 'E') && (USB1_Tx_Buf[3] == 'R')) {
printf("RCV SER CMD\r\n");
USB1Replay = 0x03;
}
if ((USB1_Tx_Buf[0] == '?') && (USB1_Tx_Buf[1] == 'C')
&& (USB1_Tx_Buf[2] == 'F') && (USB1_Tx_Buf[3] == 'G')) {
printf("RCV CFG CMD\r\n");
USB1Replay = 0x04;
}
} else {
//printf("EPS1[%d]\r\n",GetEPRxStatus(ENDP2));
USB1_Tx_Counter=USB1BufLen;
printf("EP2O[%d]\r\n",USB1_Tx_Counter);
}
}
主机的轮询发送,在main.c中,主要动作是将数据通过 USBFS_Endp_DataUp() 函数转发给USBFS 的 Port 上。
// If USB2 is connected, we will send data to USB2
if (USBFS_DevEnumStatus == 1) {
if ((USBFS_Endp_Busy[DEF_UEP3]==0)&&(USB1_Tx_Counter!=0)&&(USB1Replay==0xFF)) {
printf("A[%d]\r\n",USB1_Tx_Counter);
// Send data to USB2
USBFS_Endp_DataUp( ENDP3, &USB1_Tx_Buf[0], USB1_Tx_Counter, DEF_UEP_CPY_LOAD);
// If data length is 64, we should send a null package
if (USB1_Tx_Counter==DEF_USBD_UEP0_SIZE) {
// Wait until USB2 is free
while (USBFS_Endp_Busy[DEF_UEP3]!=0) {
}
// Send a NULL package
USBFS_Endp_DataUp( ENDP3, &USB1_Tx_Buf[0], 0, DEF_UEP_CPY_LOAD);
}
USB1_Tx_Counter=0;
// Enable USB1 Endpoint2
SetEPRxValid( ENDP2);
}
} else {
//If USB2 is NOT connected, data from USB1 would be dropped
USB1_Tx_Counter=0;
SetEPRxValid( ENDP2);
}
此外,特别命令模式处理代码如下,通过USBD_ENDPx_DataUp() 将数据返回到USBDB对的USB Port上。
if ((USB1Replay>0)&&(USB1Replay<5)) {
// Reply USB1 Command
if (USB1Replay==1) {
RPYMSG[0]='U';
RPYMSG[1]='S';
RPYMSG[2]='B';
RPYMSG[3]='1';
}
if (USB1Replay==2) {
RPYMSG[0]='0';
RPYMSG[1]='0';
RPYMSG[2]='0';
RPYMSG[3]='3';
}
if (USB1Replay==3) {
RPYMSG[0]='1';
RPYMSG[1]='2';
RPYMSG[2]='3';
RPYMSG[3]='4';
}
if (USB1Replay==4) {
if (USB2Replay!=0xFF) {
RPYMSG[0]='R';
RPYMSG[1]='E';
RPYMSG[2]='D';
RPYMSG[3]='Y';
} else {
RPYMSG[0]='N';
RPYMSG[1]='R';
RPYMSG[2]='D';
RPYMSG[3]='Y';
}
}
USBD_ENDPx_DataUp( ENDP3, &RPYMSG, sizeof(RPYMSG)); // Send to USB1
USB1Replay=0;
SetEPRxValid( ENDP2);
}
上面就是USBDB 的USB Port 处理流程,USBFS的USB Port处理逻辑相同,但是代码表达上差异很大。下面是实物:

介绍的视频
本文提到的电路图和PCB设计下载:
本文提到的完整代码下载:
最近碰到了一个困扰我很久的奇怪问题问题,最终研究发现这应该算是设计上“又不是不能用”引发的悲剧。
简单的说简单的说问题是这样的,我需要在 DSC 文件中修改一个PCD 定义:问题是这样的,我需要在 DSC 文件中修改一个PCD 定义:
gChipsetPkgTokenSpaceGuid.PcdLABZBuild|FALSE
于是将代码修改为:
#LABZDebug gChipsetPkgTokenSpaceGuid.PcdLABZBuild|FALSE
gChipsetPkgTokenSpaceGuid.PcdLABZBuild|TRUE
实际测试下来问题依旧存在,检查 Build 目录生成的中间代码最终确定是上述的修改没有起效。最终翻来覆去看代码,终于发现批处理使用如下代码来识别赋值:
findstr /C:"gChipsetPkgTokenSpaceGuid.PcdLABZBuild|FALSE" %WORKSPACE%\%PROJECT_REL_PATH%\%PROJECT_PKG%\Project.dsc >nul
因为被注释掉的代码在文件位置靠前,这个语句会把它当作正式的设定,所以导致了问题。
通常来说,本科计算机系毕业生足以编写能够实现 Parser 的代码,但是如果仅仅以“又不是不能用”作为标准来编写代码将会给使用者带来极大的麻烦。当然,如果使用者仍然遵循“又不是不能用”的逻辑来处理,还可以将代码写为如下形式,只是不知道下一个接手者是否会再撞上奇怪的问题:
gChipsetPkgTokenSpaceGuid.PcdLABZBuild|TRUE
#LABZDebug gChipsetPkgTokenSpaceGuid.PcdLABZBuild|FALSE
前面介绍了最新的 MemTest86 ,美中不足的是这个版本需要制作启动盘,这次介绍一种将它打包为一个 EFI 的方法。
基本的思路是:将完整的 MemTest86 磁盘镜像按照资源打包到一个 EFI 文件中,然后再配合之前的RamDisk 知识将这个镜像加载到内存中。这样就相当于制作的镜像文件,跳进去就可以执行了。
代码要点:
1.将之前介绍的 MemTest86 制作成一个硬件镜像,然后将这个镜像命令为MemTest2023.png
2.MyRamDisk2.inf 中给出用到的文件如下
[Sources]
MyRamDisk2.c
MyRamDisk2.idf
MemTest2023.png
3. MyRamDisk2.idf 文件内容如下
#image IMG_LOGO MemTest2023.png
4.主程序
a.首先找到当前 EFI 中的资源
//
// Retrieve HII package list from ImageHandle
//
Status = gBS->OpenProtocol (
gImageHandle,
&gEfiHiiPackageListProtocolGuid,
(VOID **) &PackageListHeader,
gImageHandle,
NULL,
EFI_OPEN_PROTOCOL_GET_PROTOCOL
);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Print(L"HII Image Package with logo not found in PE/COFF resource section\n");
return Status;
}
b.取得资源
//Step2. Parser HII Image
ImageHeader=(EFI_HII_IMAGE_PACKAGE_HDR*)(PackageListHeader+1);
ImageData=(UINT8 *)(ImageHeader+1);
c.解析资源之后拷贝到分配的内存中
// Look for Ram Disk Protocol
Status = gBS->LocateProtocol (
&gEfiRamDiskProtocolGuid,
NULL,
&MyRamDisk
);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Print(L"Couldn't find RamDiskProtocol\n");
return EFI_ALREADY_STARTED;
}
//Allocate a memory for Image
Status = gBS->AllocatePool (
EfiReservedMemoryType,
(UINTN)FileSize,
(VOID**)&StartingAddr
);
if(EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Print(L"Allocate Memory failed!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
CopyMem(StartingAddr,&ImageData[5],FileSize);
//
// Register the newly created RAM disk.
//
Status = MyRamDisk->Register (
((UINT64)(UINTN) StartingAddr),
FileSize,
&gEfiVirtualDiskGuid,
NULL,
&DevicePath
);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Print(L"Can't create RAM Disk!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
上述代码编译运行之后,会在当前系统中生成一个新的盘符,进入这个盘符之后就可以运行 MemTest86 进行内存测试了。
文本完整代码如下:
生成的 EFI 如下:
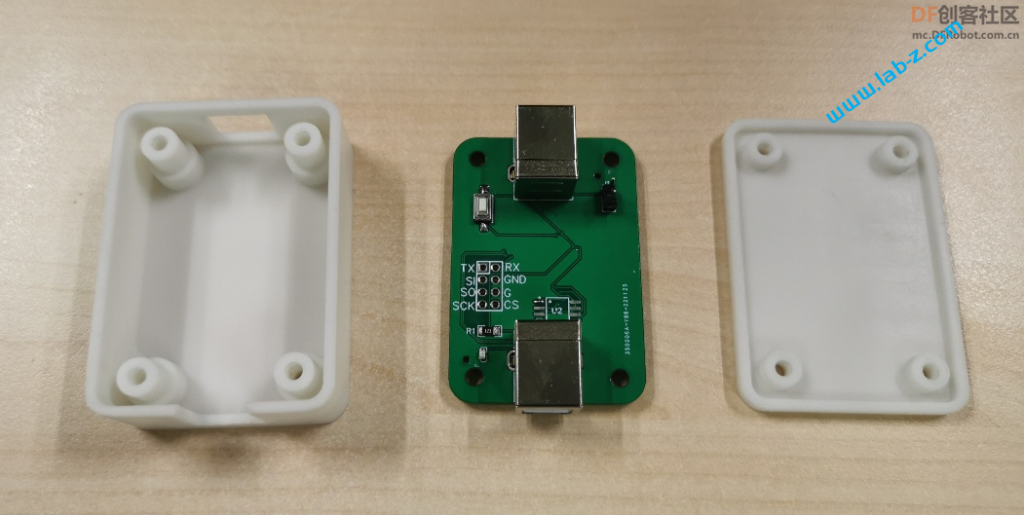
这次制作的目标是:一个插在USB接口就能不停变化颜色的灯。
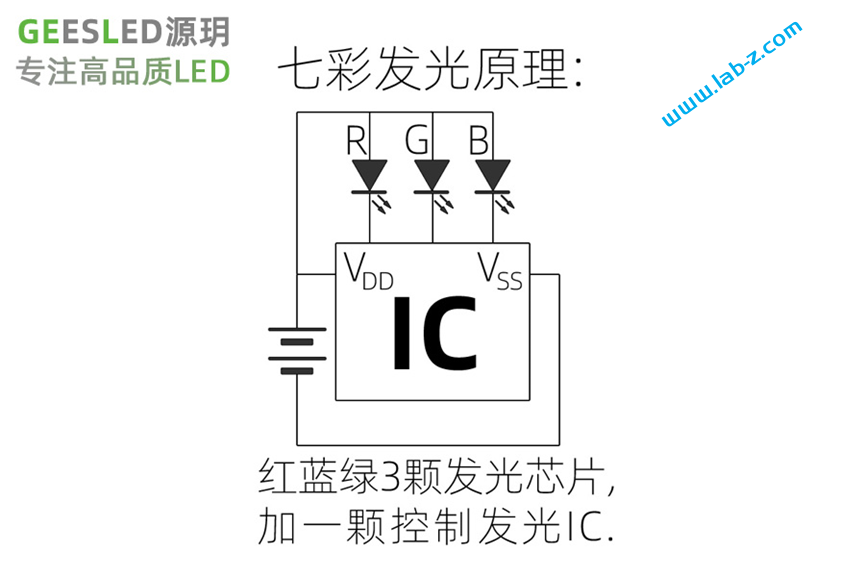
为了尽可能的压低成本,使用印刷在PCB上的USB。为了低成本实现不停变化颜色,选择淘宝上“F3圆头5mm草帽七彩慢闪led灯珠雾状装饰3v5v12伏F5七彩闪烁渐变色”这款彩灯。这款LED内置了IC,所以能够实现颜色的不停切换变化。
接下来开始电路设计,非常简单就是将LED引脚接在USB的 VCC 和GND即可。
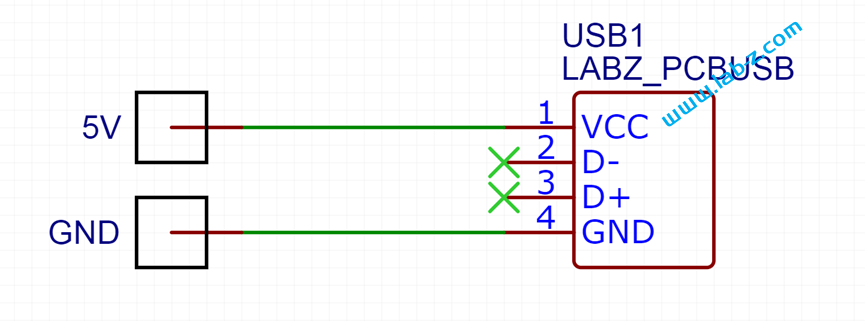
对应的USB1 封装如下:
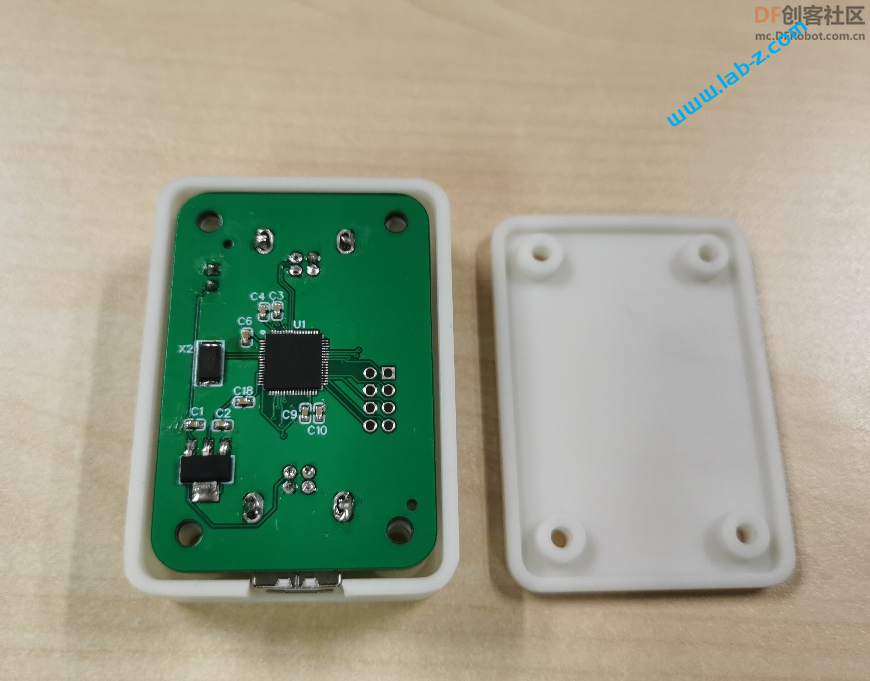
最终设计的PCB 如下:
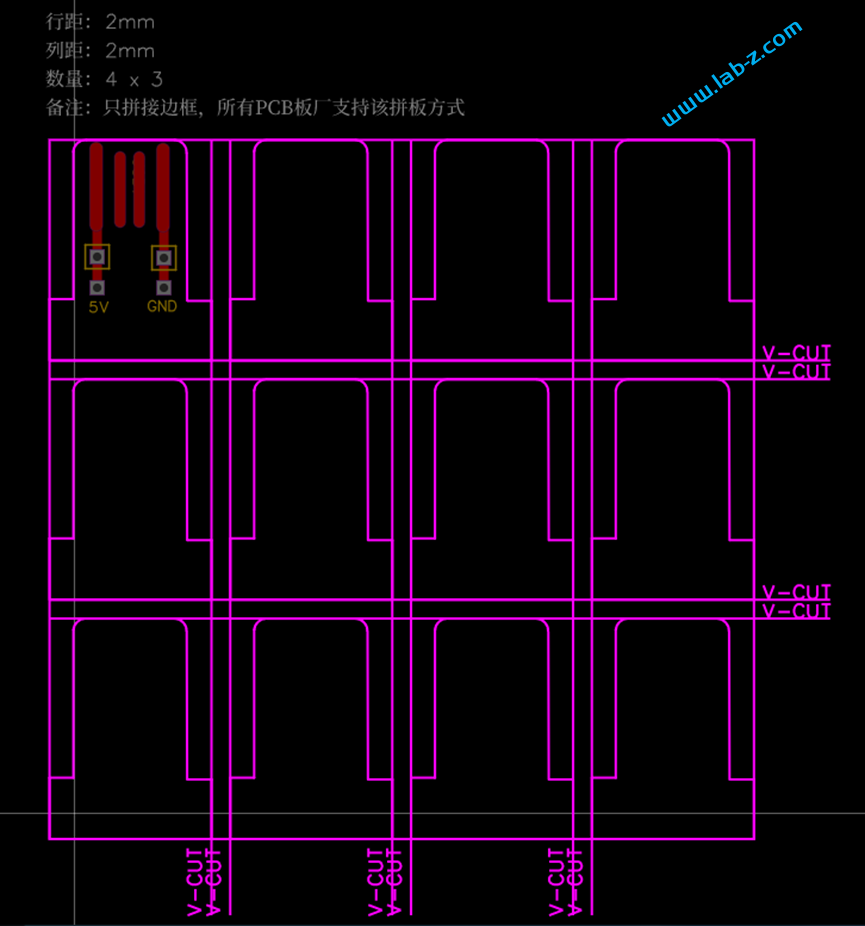
为了尽可能降低成本,特别使用V-Cut拼版,这样我们可以在一块PCB上容纳尽量多的PCB。同时需要注意的是:对于嘉立创来说,如果每一个PCB长度或者宽度小于15mm,那么会加收100元的费用,因此,如果有可能尽量不要过窄或者过短。
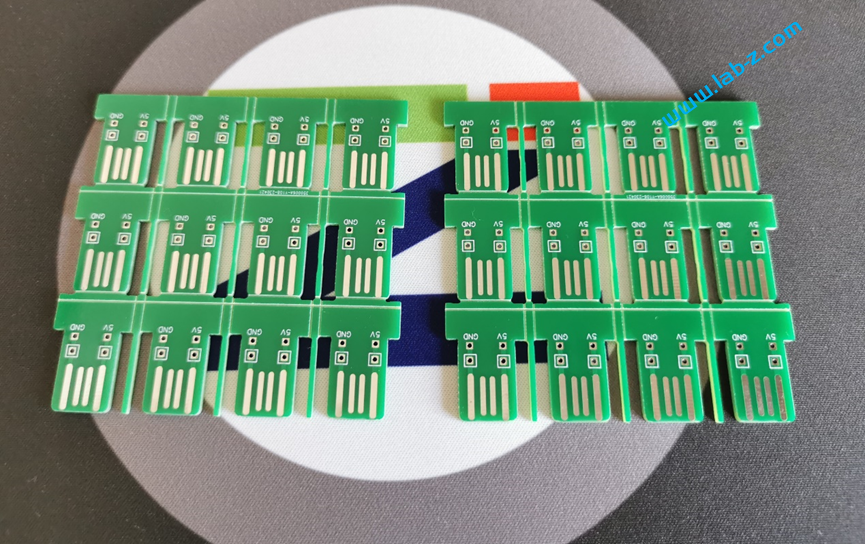
PCB制作之后是这样的:
需要注意的是:理论上如果直接制作厚度为2.0mm的PCB 那么直接可以插入USB接口的。但是制作PCB时需要增加费用,因此选择制作1.6mm常规厚度的PCB ,拿到手后在USB线路位置自行粘贴剪裁后的信用卡、SIM卡之类的塑料卡片增加厚度。
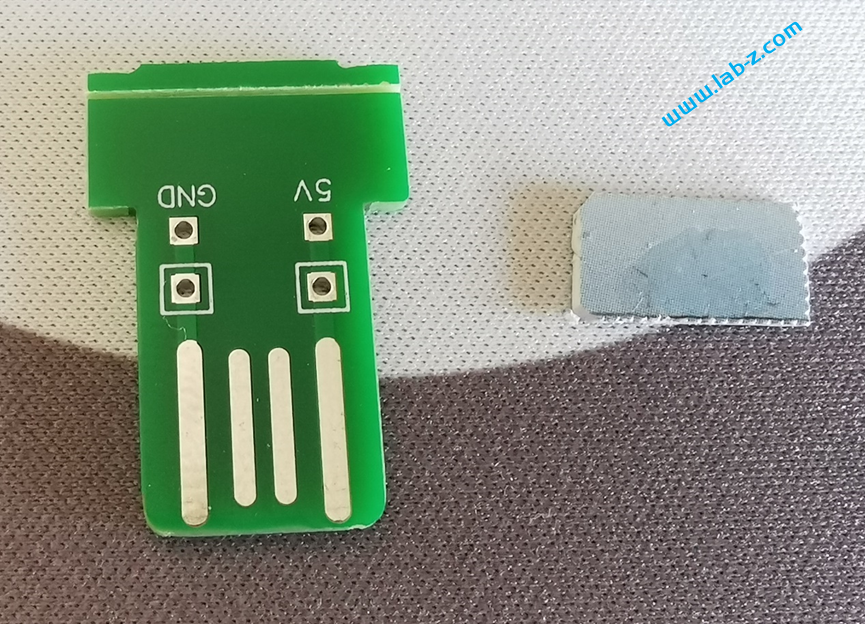
我使用502胶水粘贴固定
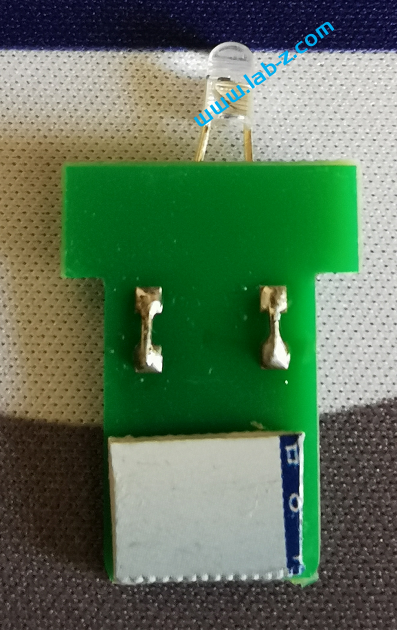
正面:
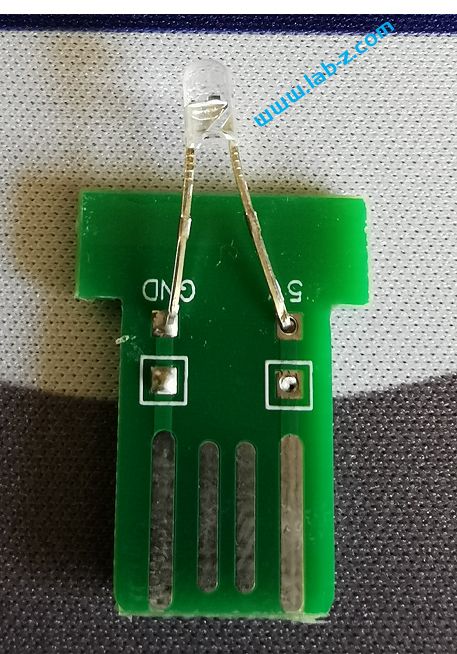
工作的视频可以在下面看到:
总结省钱妙招:
最终花费:47.43 元制作12*6=60个PCB, LED 费用为 18元100个。因此,平均下来每个0.97元。
完整的电路图和PCB 下载(立创EDA)
参考:
1. https://detail.tmall.com/item.htm?_u=dkf8s92d31&id=624355880993&spm=a1z09.2.0.0.26642e8dewUEbx