前面【参考1】提到了 StartImage 加载 CLib 编写Application 出错的原因,这篇文章介绍如何解决这个问题。
根据原因来看是因为找不到提供 Parameters 的Protocol,那么我们在调用之前给被加载的Application 装上需要的Protocol即可。安装 Protocol 需要用到 InstallProtocollInterface,具体定义如下【参考2】:

欲安装的 Protocol 实例则是从加载程序(Exec6)上面取下来的。
没有多少人愿意看大篇幅的代码,我这里列下最关键的部分:
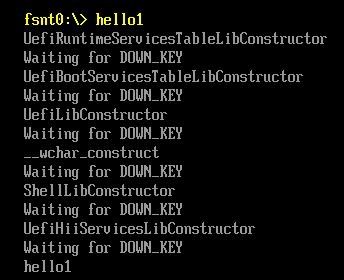
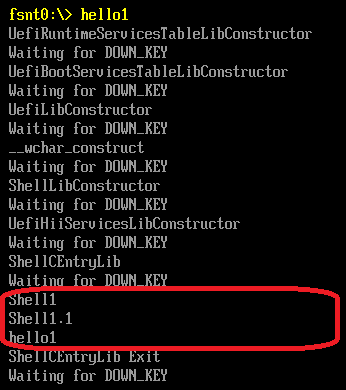
首先,取出当前的 Shell Interface, 不同的环境下还可以使用 Shell Parameter Protocol , NT32 环境下只支持前者
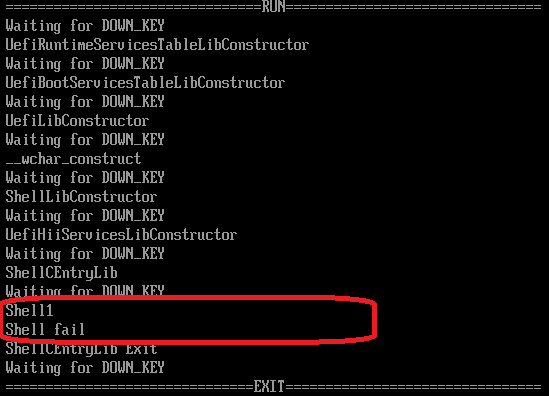
//如果你在实体机上发现有问题,那么可以考虑这段代码的问题
Status = gBS->OpenProtocol(gImageHandle,
&gEfiShellInterfaceGuid,
(VOID **)&EfiShellInterface,
gImageHandle,
NULL,
EFI_OPEN_PROTOCOL_GET_PROTOCOL
);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Shell Parameters Protocol not Found!\r\n",Status);
return (Status);
}
//之后,将取下来的 Protocol 安装给被加载的 Application
Status = gBS->InstallProtocolInterface (
&NewHandle,
&gEfiShellInterfaceGuid,
EFI_NATIVE_INTERFACE,
EfiShellInterface
);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Protocol Interface Installed fail!\r\n",Status);
return (Status);
}
最后,安装之后不能忘记 Uninstall,还要调用一下,特别注意第一个参数传递的不是指针。
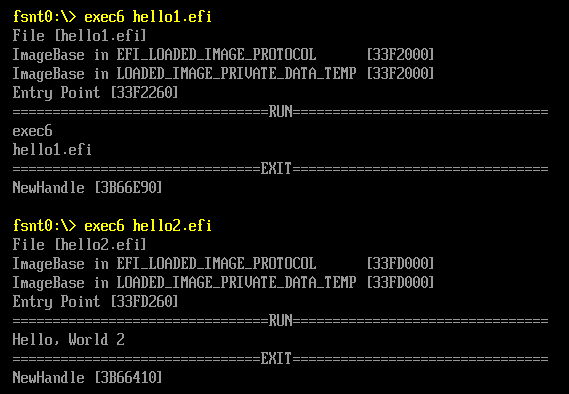
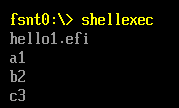
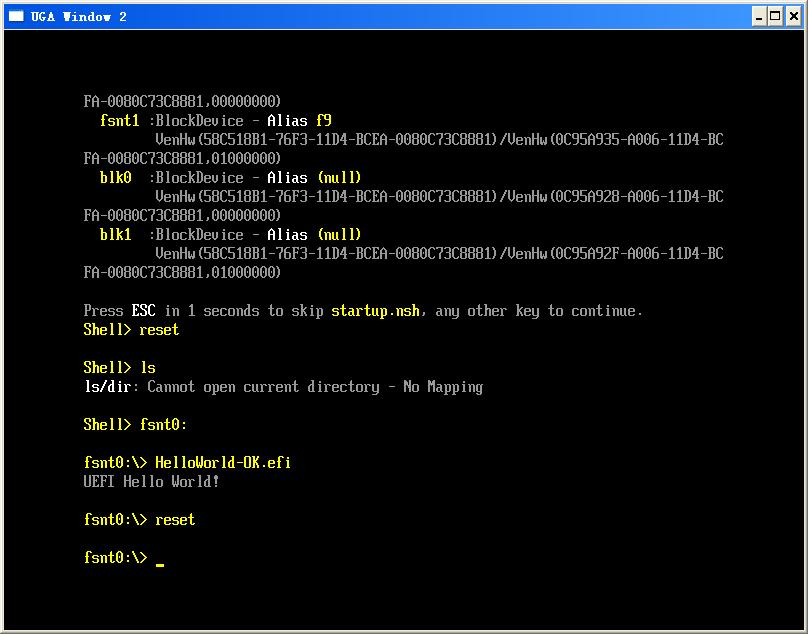
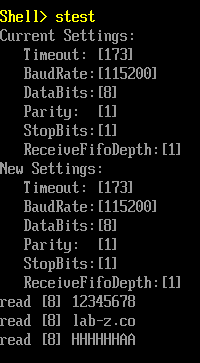
运行结果,可以看出 Hello1和 Hello2都可以被正常加载运行:
看到这里,这篇文章就可以结束了,下面列出 Exec6 的代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <wchar.h>
#include <Protocol/EfiShell.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
extern EFI_SHELL_PROTOCOL *gEfiShellProtocol;
extern EFI_SHELL_ENVIRONMENT2 *mEfiShellEnvironment2;
extern EFI_HANDLE gImageHandle;
typedef struct {
UINTN Signature;
/// Image handle
EFI_HANDLE Handle;
/// Image type
UINTN Type;
/// If entrypoint has been called
BOOLEAN Started;
/// The image's entry point
EFI_IMAGE_ENTRY_POINT EntryPoint;
/// loaded image protocol
EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL Info;
/// Location in memory
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS ImageBasePage;
} LOADED_IMAGE_PRIVATE_DATA_TEMP;
#define _CR(Record, TYPE, Field) ((TYPE *) ((CHAR8 *) (Record) - (CHAR8 *) &(((TYPE *) 0)->Field)))
#define LOADED_IMAGE_PRIVATE_DATA_FROM_THIS(a) \
_CR(a, LOADED_IMAGE_PRIVATE_DATA_TEMP, Info)
/**
GET DEVICEPATH
**/
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *
EFIAPI
ShellGetDevicePath (
IN CHAR16 * CONST DeviceName OPTIONAL
)
{
//
// Check for UEFI Shell 2.0 protocols
//
if (gEfiShellProtocol != NULL) {
return (gEfiShellProtocol->GetDevicePathFromFilePath(DeviceName));
}
//
// Check for EFI shell
//
if (mEfiShellEnvironment2 != NULL) {
return (mEfiShellEnvironment2->NameToPath(DeviceName));
}
return (NULL);
}
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *DevicePath;
EFI_HANDLE NewHandle;
EFI_STATUS Status;
LOADED_IMAGE_PRIVATE_DATA_TEMP *private = NULL;
UINTN ExitDataSizePtr;
EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL *ImageInfo = NULL;
EFI_SHELL_INTERFACE *EfiShellInterface=NULL;
if (Argc!=2) {
Print(L"Usage: Exec4 FileName\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
Print(L"File [%s]\n",Argv[1]);
DevicePath=ShellGetDevicePath(Argv[1]);
//
// Load the image with:
// FALSE - not from boot manager and NULL, 0 being not already in memory
//
Status = gBS->LoadImage(
FALSE,
gImageHandle,
DevicePath,
NULL,
0,
&NewHandle);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
if (NewHandle != NULL) {
gBS->UnloadImage(NewHandle);
}
Print(L"Error during LoadImage [%X]\n",Status);
return (Status);
}
Status = gBS -> HandleProtocol (
NewHandle,
&gEfiLoadedImageProtocolGuid,
&ImageInfo
);
private = LOADED_IMAGE_PRIVATE_DATA_FROM_THIS(ImageInfo);
Print(L"ImageBase in EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL [%lX]\n",ImageInfo->ImageBase);
Print(L"ImageBase in LOADED_IMAGE_PRIVATE_DATA_TEMP [%lX]\n",private->ImageBasePage);
Print(L"Entry Point [%lX]\n",private->EntryPoint);
Status = gBS->OpenProtocol(gImageHandle,
&gEfiShellInterfaceGuid,
(VOID **)&EfiShellInterface,
gImageHandle,
NULL,
EFI_OPEN_PROTOCOL_GET_PROTOCOL
);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Shell Parameters Protocol not Found!\r\n",Status);
return (Status);
}
Status = gBS->InstallProtocolInterface (
&NewHandle,
&gEfiShellInterfaceGuid,
EFI_NATIVE_INTERFACE,
EfiShellInterface
);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Protocol Interface Installed fail!\r\n",Status);
return (Status);
}
Print(L"================================RUN================================\r\n",Status);
//
// now start the image, passing up exit data if the caller requested it
//
Status = gBS->StartImage(
NewHandle,
&ExitDataSizePtr,
NULL
);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
if (NewHandle != NULL) {
gBS->UnloadImage(NewHandle);
}
Print(L"Error during StartImage [%X]\r\n",Status);
return (Status);
}
Print(L"===============================EXIT================================\r\n",Status);
Status = gBS->UninstallProtocolInterface (
NewHandle,
&gEfiShellInterfaceGuid,
EfiShellInterface
);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Protocol Interface Uninstalled fail!\r\n",Status);
return (Status);
}
gBS->UnloadImage (NewHandle);
Print(L"NewHandle [%lX]\n",NewHandle);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
完整代码下载:
exec6
至此,终于回答了 StartImage 执行Application 的问题,如果你发现本文有任何问题欢迎给我留言,或者你有什么其他问题,同样可以给我发 e-Mail。
就是这样。
参考:
1. http://www.lab-z.com/stu85/ StartImage CLib
2. Uefi Spec 2.4 P153