很多时候我们编写的一些工具需要支持暂停的功能,比如:ls 列出的文件名时最好能够响应用户的按键,暂停一下以便用户查看结果。查看了一下Shell方面的代码,可以通过 Shell Environment 2 提供的函数来实现。
当然,我不愿意使用庞大的 Shell Library,选择性的提取一些代码就OK
//
// PauseTest.c
//
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiApplicationEntryPoint.h>
#include <Library/BaseMemoryLib.h>
#define SHELL_INTERFACE_PROTOCOL \
{ \
0x47c7b223, 0xc42a, 0x11d2, 0x8e, 0x57, 0x0, 0xa0, 0xc9, 0x69, 0x72, 0x3b \
}
EFI_GUID ShellInterfaceProtocol = SHELL_INTERFACE_PROTOCOL;
EFI_GUID SEGuid = EFI_SE_EXT_SIGNATURE_GUID;
//
// The shell environment is provided by a driver. The shell links to the
// shell environment for services. In addition, other drivers may connect
// to the shell environment and add new internal command handlers, or
// internal protocol handlers.
//
#define SHELL_ENVIRONMENT_INTERFACE_PROTOCOL \
{ \
0x47c7b221, 0xc42a, 0x11d2, 0x8e, 0x57, 0x0, 0xa0, 0xc9, 0x69, 0x72, 0x3b \
}
EFI_GUID ShellEnvProtocol = SHELL_ENVIRONMENT_INTERFACE_PROTOCOL;
#define EFI_OUTPUT_PAUSE 0x00000002
typedef struct {
SHELLENV_EXECUTE Execute; // Execute a command line
SHELLENV_GET_ENV GetEnv; // Get an environment variable
SHELLENV_GET_MAP GetMap; // Get mapping tables
SHELLENV_ADD_CMD AddCmd; // Add an internal command handler
SHELLENV_ADD_PROT AddProt; // Add protocol info handler
SHELLENV_GET_PROT GetProt; // Get the protocol ID
SHELLENV_CUR_DIR CurDir;
SHELLENV_FILE_META_ARG FileMetaArg;
SHELLENV_FREE_FILE_LIST FreeFileList;
//
// The following services are only used by the shell itself
//
SHELLENV_NEW_SHELL NewShell;
SHELLENV_BATCH_IS_ACTIVE BatchIsActive;
SHELLENV_FREE_RESOURCES FreeResources;
} EFI_SHELL_ENVIRONMENT;
EFI_SHELL_INTERFACE *SI;
EFI_SHELL_ENVIRONMENT *SE;
EFI_SHELL_ENVIRONMENT2 *SE2;
EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
//Copy from \Shell\Library\Misc.c
BOOLEAN
GrowBuffer (
IN OUT EFI_STATUS *Status,
IN OUT VOID **Buffer,
IN UINTN BufferSize
)
/*++
Routine Description:
Helper function called as part of the code needed
to allocate the proper sized buffer for various
EFI interfaces.
Arguments:
Status - Current status
Buffer - Current allocated buffer, or NULL
BufferSize - Current buffer size needed
Returns:
TRUE - if the buffer was reallocated and the caller
should try the API again.
--*/
{
BOOLEAN TryAgain;
//
// If this is an initial request, buffer will be null with a new buffer size
//
if (NULL == *Buffer && BufferSize) {
*Status = EFI_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL;
}
//
// If the status code is "buffer too small", resize the buffer
//
TryAgain = FALSE;
if (*Status == EFI_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL) {
if (*Buffer) {
FreePool (*Buffer);
}
*Buffer = AllocateZeroPool (BufferSize);
if (*Buffer) {
TryAgain = TRUE;
} else {
*Status = EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES;
}
}
//
// If there's an error, free the buffer
//
if (!TryAgain && EFI_ERROR (*Status) && *Buffer) {
FreePool (*Buffer);
*Buffer = NULL;
}
return TryAgain;
}
//Copy from \Shell\Library\Handle.c
EFI_STATUS
LocateHandle (
IN EFI_LOCATE_SEARCH_TYPE SearchType,
IN EFI_GUID * Protocol OPTIONAL,
IN VOID *SearchKey OPTIONAL,
IN OUT UINTN *NoHandles,
OUT EFI_HANDLE **Buffer
)
/*++
Routine Description:
Function returns an array of handles that support the requested protocol
in a buffer allocated from pool.
Arguments:
SearchType - Specifies which handle(s) are to be returned.
Protocol - Provides the protocol to search by.
This parameter is only valid for SearchType ByProtocol.
SearchKey - Supplies the search key depending on the SearchType.
NoHandles - The number of handles returned in Buffer.
Buffer - A pointer to the buffer to return the requested array of
handles that support Protocol.
Returns:
EFI_SUCCESS - The result array of handles was returned.
EFI_NOT_FOUND - No handles match the search.
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES - There is not enough pool memory to store the matching results.
--*/
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
UINTN BufferSize;
//
// Initialize for GrowBuffer loop
//
Status = EFI_SUCCESS;
*Buffer = NULL;
BufferSize = 50 * sizeof (EFI_HANDLE);
//
// Call the real function
//
while (GrowBuffer (&Status, (VOID **) Buffer, BufferSize)) {
Status = gBS->LocateHandle (
SearchType,
Protocol,
SearchKey,
&BufferSize,
*Buffer
);
}
*NoHandles = BufferSize / sizeof (EFI_HANDLE);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
*NoHandles = 0;
}
return Status;
}
INTN
CompareGuidx (
IN EFI_GUID *Guid1,
IN EFI_GUID *Guid2
)
/*++
Routine Description:
Compares to GUIDs
Arguments:
Guid1 - guid to compare
Guid2 - guid to compare
Returns:
= 0 if Guid1 == Guid2
!= 0 if Guid1 != Guid2
--*/
{
INT32 *g1;
INT32 *g2;
INT32 r;
//
// Compare 32 bits at a time
//
g1 = (INT32 *) Guid1;
g2 = (INT32 *) Guid2;
r = g1[0] - g2[0];
r |= g1[1] - g2[1];
r |= g1[2] - g2[2];
r |= g1[3] - g2[3];
return r;
}
// Copy from \Shell\Library\Init.c
EFI_STATUS
LibInitializeShellApplication (
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *SystemTable
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_HANDLE *HandleBuffer;
UINTN HandleNum;
UINTN HandleIndex;
EFI_GUID SESGuid = EFI_SE_EXT_SIGNATURE_GUID;
//
// Connect to the shell interface
//
Status = gBS->HandleProtocol (ImageHandle, &ShellInterfaceProtocol, (VOID *) &SI);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Print (L"InitShellApp: Application not started from Shell\n");
gBS->Exit (ImageHandle, Status, 0, NULL);
}
//
// Connect to the shell environment
//
Status = gBS->HandleProtocol (
ImageHandle,
&ShellEnvProtocol,
(VOID *) &SE2
);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status) || !(CompareGuid (&SE2->SESGuid, &SESGuid) == 0 &&
(SE2->MajorVersion > EFI_SHELL_MAJOR_VER ||
(SE2->MajorVersion == EFI_SHELL_MAJOR_VER && SE2->MinorVersion >=
EFI_SHELL_MINOR_VER))
)
) {
Status = LocateHandle (
ByProtocol,
&ShellEnvProtocol,
NULL,
&HandleNum,
&HandleBuffer
);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Print (L"InitShellApp: 1Shell environment interfaces not found\n");
gBS->Exit (ImageHandle, Status, 0, NULL);
}
Status = EFI_NOT_FOUND;
for (HandleIndex = 0; HandleIndex < HandleNum; HandleIndex++) {
gBS->HandleProtocol (
HandleBuffer[HandleIndex],
&ShellEnvProtocol,
(VOID *) &SE2
);
if (CompareGuidx (&SE2->SESGuid, &SESGuid) == 0)
{
Status = EFI_SUCCESS;
break;
}
}
FreePool (HandleBuffer);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Print (L"InitShellApp: 2Shell environment interfaces not found\n");
gBS->Exit (ImageHandle, Status, Status, NULL);
}
}
SE = (EFI_SHELL_ENVIRONMENT *) SE2;
//
// Done with init
//
return Status;
}
//
// Entry point function
//
EFI_STATUS
UefiMain (
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *SystemTable
)
{
INTN i;
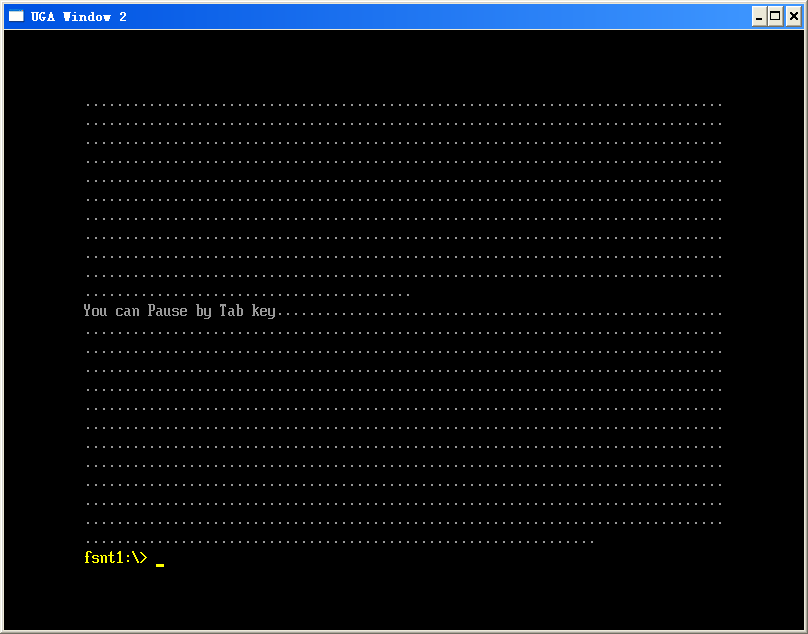
Print(L"You can't Pause by Tab key\n");
for (i=0;i<1000;i++)
{
Print(L".");
}
Print(L".\n");
gBS = SystemTable -> BootServices;
LibInitializeShellApplication (ImageHandle,SystemTable);
SE2->SetKeyFilter(SE2->GetKeyFilter() | EFI_OUTPUT_PAUSE);
Print(L"You can Pause by Tab key");
for (i=0;i<1000;i++)
{
Print(L".");
}
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
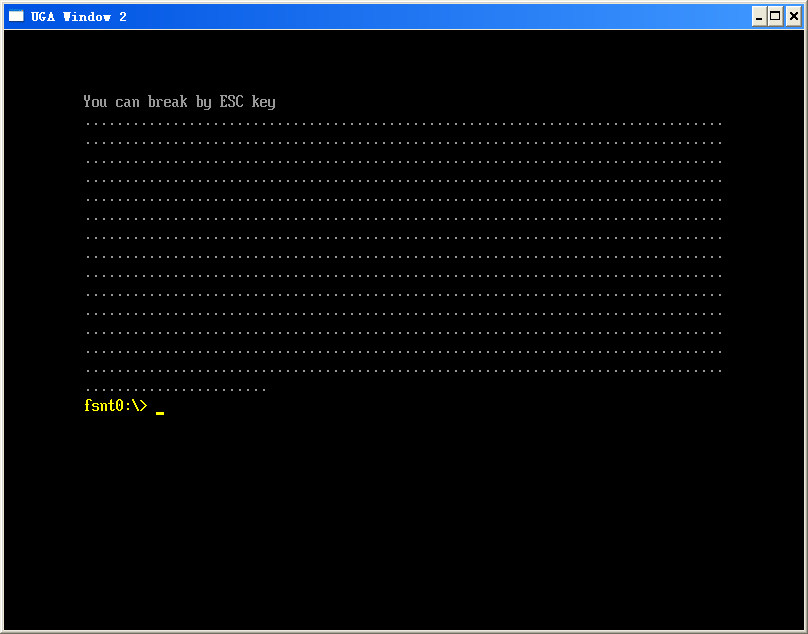
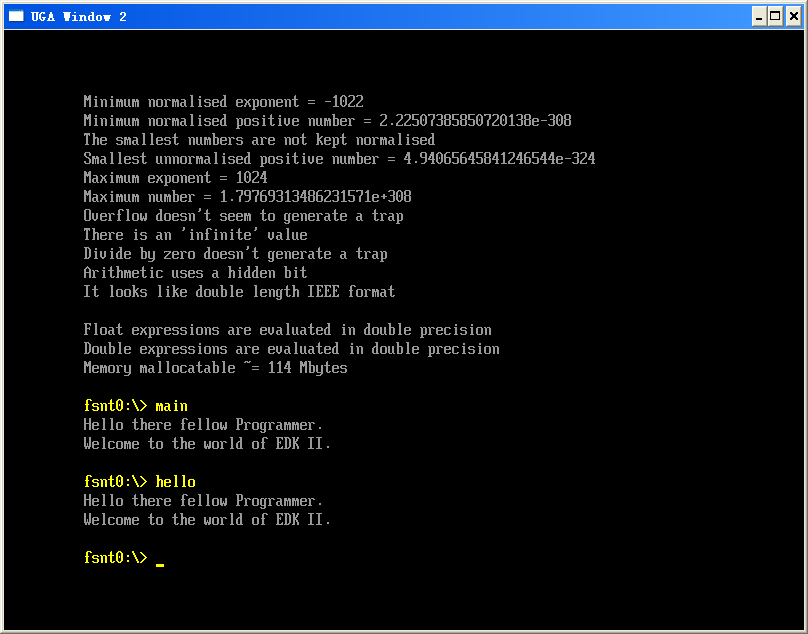
上面的代码演示了使用 Pause Break键来暂停输出的功能。
代码在这里下载:
PauseTest